
Challenges in Hemp Filament Production
Hemp is a sustainable and eco-friendly material that has gained popularity in various industries around the world. One of the emerging applications of hemp is in the production of filaments for 3D printing. However, creating high-quality hemp filaments that are water repellent can be a challenging task for manufacturers.
The water repellency of filaments is a crucial factor that affects their functionality and durability in various applications. In this technical guide, we will explore the science behind water repellency in filament manufacturing and provide a step-by-step process for creating water-repellent hemp filaments.
Understanding Water Repellency in Filament Manufacturing
Water repellency refers to the ability of a material to resist the penetration of water or other liquids. In filament manufacturing, water repellency is achieved by modifying the surface properties of the filament to create a hydrophobic barrier that repels water.
The surface properties of a filament are determined by factors such as its chemical composition, surface roughness, and surface energy. Modifying these factors can alter the filament’s interaction with water and improve its water repellency.
Factors Affecting Water Repellency of Hemp Filaments
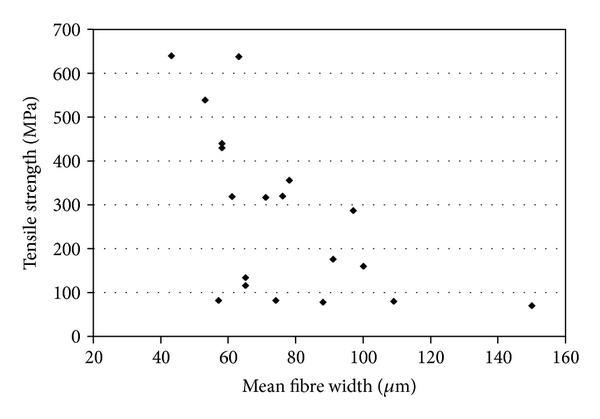
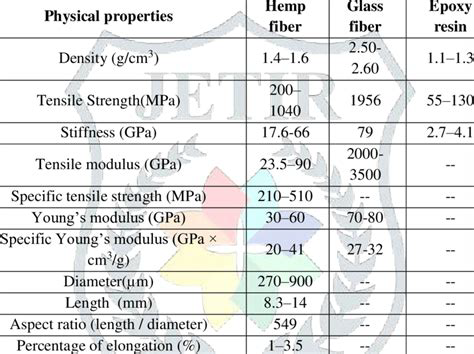
The water repellency of hemp filaments is influenced by several factors, including the type of hemp used, the processing method, and the filament formulation. The type of hemp used can affect the chemical composition and surface properties of the filament, which in turn impacts its water repellency.
The processing method also plays a crucial role in the water repellency of hemp filaments. Extrusion parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rate can affect the surface roughness and surface energy of the filament, which can impact its water repellency.
Furthermore, the filament formulation, including the type and amount of additives used, can affect the water repellency of hemp filaments. Additives such as surfactants and hydrophobic agents can improve the water repellency of the filament.
Developing Water-Repellent Hemp Filament Formulations
To create water-repellent hemp filaments, manufacturers can modify the formulation of the filament by adding hydrophobic agents, such as silicone or fluoropolymer, to the filament blend. These agents create a hydrophobic barrier on the surface of the filament, which repels water.
The amount and type of hydrophobic agents used will depend on the desired water repellency of the filament. However, it is essential to strike a balance between water repellency and other properties such as mechanical strength and printability.
Testing Water Repellency of Hemp Filaments
To evaluate the water repellency of hemp filaments, manufacturers can perform water droplet tests on the filament’s surface. This involves placing a droplet of water on the filament’s surface and observing how it behaves.
A water-repellent filament will cause the water droplet to bead up and roll off the surface, while a non-repellent filament will cause the droplet to spread out and be absorbed by the surface.
Optimizing Filament Extrusion Parameters for Water-Repellent Filaments
The extrusion parameters used in the filament manufacturing process can impact the water repellency of the final product. By adjusting parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rate, manufacturers can optimize the surface properties of the filament to improve water repellency.
For example, reducing the extrusion temperature can increase the surface roughness of the filament, which can improve its water repellency.
The Role of Additives in Creating Water-Repellent Hemp Filaments
Additives such as surfactants and hydrophobic agents can improve the water repellency of hemp filaments. Surfactants can reduce the surface tension of the filament, making it easier for hydrophobic agents to adhere to the surface.
Hydrophobic agents such as silicone or fluoropolymer can create a hydrophobic barrier on the surface of the filament, which repels water. However, it is essential to carefully select the type and amount of additives used to ensure that they do not negatively impact other properties of the filament, such as mechanical strength and printability.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Hemp Filament Water Repellency
Manufacturers may encounter issues such as inconsistent water repellency or poor printability when creating water-repellent hemp filaments. To troubleshoot these issues, it is essential to carefully evaluate the filament formulation and extrusion parameters to identify potential issues.
For example, inconsistent water repellency may be caused by uneven distribution of additives in the filament blend or inadequate mixing of the filament ingredients. Poor printability may be caused by excessive hydrophobicity, which can cause the filament to clump or clog the extruder.
Evaluating the Economic and Environmental Benefits of Water-Repellent Hemp Filaments
Water-repellent hemp filaments offer several economic and environmental benefits. They are a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional filaments, which are often made from non-renewable resources.
Furthermore, water-repellent hemp filaments can improve the durability and functionality of products in various applications, reducing the need for maintenance and replacement. This can result in cost savings for manufacturers and end-users.
Applications of Water-Repellent Hemp Filaments in Various Industries
Water-repellent hemp filaments can be used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. In the automotive industry, water-repellent hemp filaments can be used for components such as door handles, dashboard panels, and interior trim.
In the aerospace industry, water-repellent hemp filaments can be used for components such as air ducts, seating components, and interior panels. In the consumer goods industry, water-repellent hemp filaments can be used for products such as outdoor furniture, sportswear, and camping gear.
Future Directions in Hemp Filament Research and Development
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials continues to grow, there is a need for ongoing research and development in hemp filament production. Future research may focus on developing new methods for creating water-repellent hemp filaments, optimizing extrusion parameters, and identifying new applications for hemp filaments in various industries.
Achieving Water-Repellent Hemp Filaments through Technical Expertise
Creating water-repellent hemp filaments requires technical expertise and careful attention to the filament formulation and extrusion parameters. By understanding the factors that affect water repellency and developing effective formulations and extrusion parameters, manufacturers can create high-quality hemp filaments that meet the needs of various industries. The economic and environmental benefits of water-repellent hemp filaments make them a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional filaments, with numerous applications in various industries.























 Home(1)
Home(1)




