
Small-Scale Hemp Projects
Small-scale hemp projects have gained popularity in recent years due to the increasing demand for hemp products such as CBD oil, hemp seeds, and hemp fiber. These projects are typically run by small-scale farmers and entrepreneurs who are looking to tap into the lucrative hemp market. While large-scale hemp farming operations require significant investments in infrastructure and equipment, small-scale projects offer a more accessible entry point for those with limited resources.
In this article, we will explore the prospects of small-scale hemp projects, the techniques involved in hemp farming, harvesting, processing, and seed storage, as well as the industrial applications of hemp fiber and oil. Additionally, we will delve into the role of technology in small-scale hemp projects and how it can be leveraged to maximize yields and efficiency.
The Prospects of Small-Scale Hemp Projects
The hemp industry has seen exponential growth in recent years, with the global market expected to reach $18.3 billion by 2025. This growth can be attributed to the legalization of hemp cultivation in several countries and the increasing demand for hemp-derived products such as CBD oil, which is believed to have medicinal properties. Small-scale hemp projects offer an opportunity for farmers and entrepreneurs to tap into this growing market and generate revenue.
Small-scale hemp projects have several advantages over large-scale operations. They require less capital investment and can be started with fewer resources. They also offer greater flexibility and allow for experimentation with different hemp strains and cultivation techniques. Furthermore, small-scale projects are more sustainable and environmentally friendly, as they promote biodiversity and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Understanding the Hemp Industry
Before embarking on a small-scale hemp project, it is essential to understand the hemp industry and the different types of hemp products. Hemp is a versatile plant that can be used for various applications, including food, textiles, paper, construction, and biofuels. The hemp plant contains over 100 cannabinoids, including CBD and THC, which have different effects on the body.
Hemp cultivation requires specific conditions, including fertile soil, adequate water supply, and proper lighting. The plant has a relatively short growing season, usually between 70-140 days, depending on the strain. It is also essential to adhere to local regulations and obtain the necessary permits and licenses to cultivate, harvest, and sell hemp.
Hemp Farming Techniques for Small-Scale Projects
Small-scale hemp farming requires careful planning and execution to maximize yields and ensure the quality of the crop. The first step is to select the appropriate hemp strain based on the intended use of the plant. This will determine the planting date, spacing, and other cultivation practices.
Hemp can be grown using various techniques, including direct seeding, transplanting, and cloning. Direct seeding is the most common technique and involves planting the seeds directly into the soil. Transplanting involves growing the seedlings in a nursery before transplanting them into the field. Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mature plant and rooting them to produce identical clones.
Hemp cultivation also requires proper soil preparation, fertilization, and irrigation. The plant requires fertile soil with adequate drainage and a pH between 6-7.5. Hemp responds well to organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, and requires regular watering, especially during the early growth stages.
Harvesting and Processing Hemp for Small-Scale Projects
Harvesting and processing are crucial stages in small-scale hemp projects, as they determine the quality and value of the final product. Hemp is typically harvested when the plants are mature and the seeds have reached full maturity. The timing of the harvest will depend on the intended use of the plant. For instance, if the plant is grown for fiber, it should be harvested before the seeds develop fully.
Hemp can be harvested using various techniques, including hand harvesting, mechanical harvesting, and combine harvesting. Hand harvesting is labor-intensive but allows for greater control over the harvesting process. Mechanical harvesting is more efficient but can damage the plant and reduce the quality of the fiber. Combine harvesting is the most efficient technique and is commonly used for large-scale operations.
Processing hemp involves removing the seeds, leaves, and flowers from the stalks and stems. The remaining material can be processed further to produce hemp fiber, which can be used for textiles and construction, or hemp biomass, which can be used for biofuels and other industrial applications.
Hemp Seed Storage and Germination Techniques
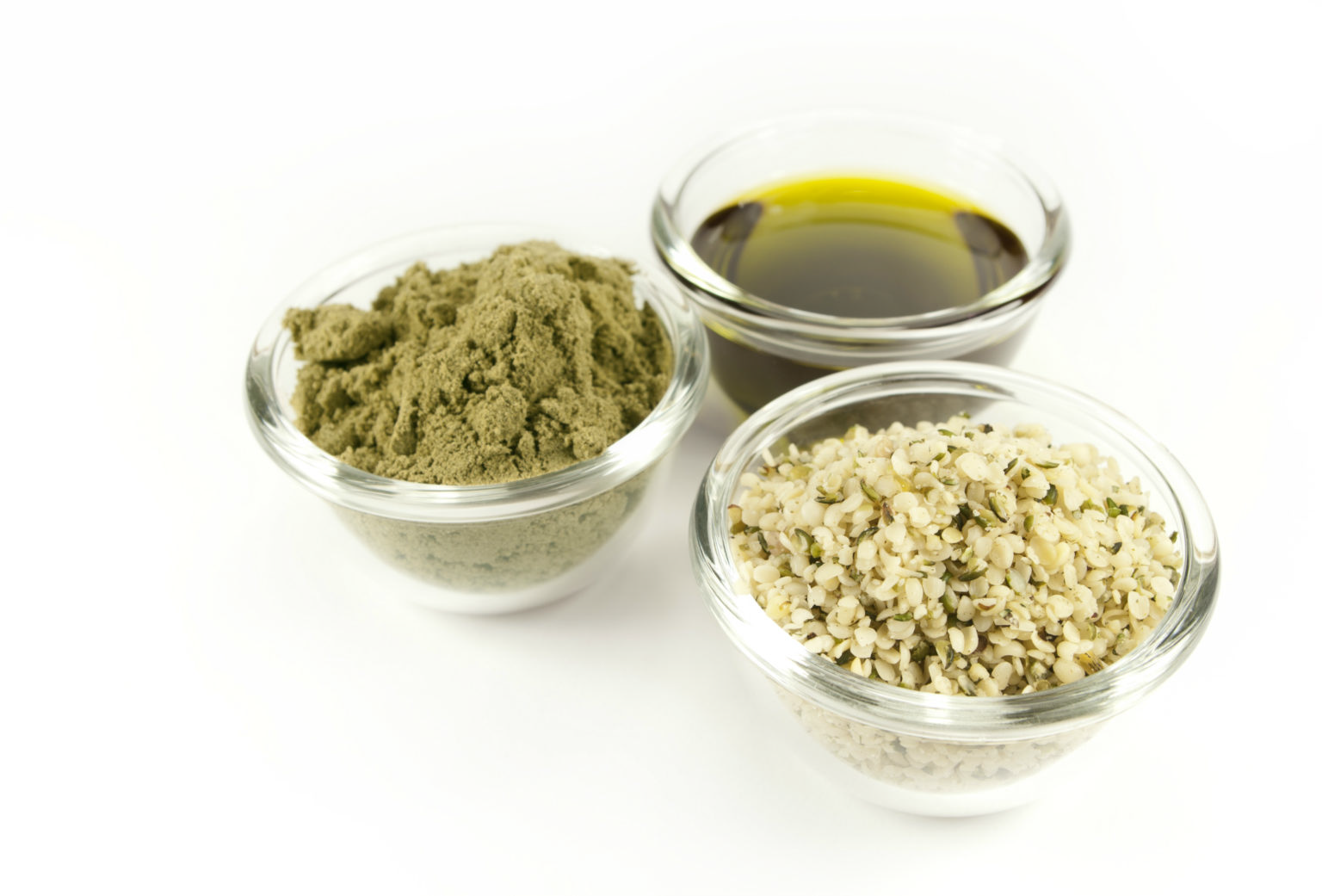
Hemp seeds are a valuable commodity used for food, oil, and animal feed. Proper seed storage and germination techniques are critical to ensure the quality and viability of the seeds. Hemp seeds should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and moisture. They can be stored for up to five years without losing viability.
Hemp seeds can be germinated using various techniques, including direct seeding, transplanting, and cloning. Direct seeding is the most common technique and involves planting the seeds directly into the soil. Transplanting involves growing the seedlings in a nursery before transplanting them into the field. Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mature plant and rooting them to produce identical clones.
Industrial Applications of Small-Scale Hemp Projects
Hemp has numerous industrial applications, including textiles, paper, construction, and biofuels. Small-scale hemp projects can tap into these applications and generate revenue. Hemp fiber can be processed further to produce textiles, rope, and paper. Hemp biomass can be used for biofuels, animal feed, and other industrial applications.
Hemp oil is also a valuable commodity used for food, cosmetic, and medicinal purposes. Small-scale hemp projects can produce high-quality hemp oil using various extraction techniques, including cold-pressed extraction, solvent extraction, and CO2 extraction.
Hemp Fiber Processing Techniques for Small-Scale Projects
Hemp fiber processing involves removing the fiber from the stalks and stems and processing it further to produce textiles, rope, and paper. Small-scale hemp projects can use various techniques, including retting, decortication, and scutching, to process hemp fiber.
Retting involves soaking the hemp stalks in water to loosen the fibers from the stem. Decortication involves separating the fibers from the woody core using a mechanical decorticator. Scutching involves beating the fibers to remove any remaining woody material.
Extraction Techniques for Small-Scale Hemp Projects
Extraction is a crucial stage in producing hemp oil and other hemp-derived products. Small-scale hemp projects can use various extraction techniques, including cold-pressed extraction, solvent extraction, and CO2 extraction. Cold-pressed extraction involves using a mechanical press to extract the oil. Solvent extraction involves using a solvent, such as ethanol or hexane, to extract the oil. CO2 extraction involves using supercritical CO2 to extract the oil.
Small-Scale Hemp Oil Production Techniques
Hemp oil is a valuable commodity used for food, cosmetics, and medicinal purposes. Small-scale hemp projects can produce high-quality hemp oil using various extraction techniques, including cold-pressed extraction, solvent extraction, and CO2 extraction. The oil can be further processed to remove any impurities and to increase its potency.
The Role of Technology in Small-Scale Hemp Projects
Technology can play a significant role in maximizing yields and efficiency in small-scale hemp projects. Various technologies, such as precision agriculture, drones, and IoT sensors, can be used to monitor and optimize crop growth, irrigation, and fertilization. Additionally, blockchain technology can be used to track the supply chain and ensure the authenticity and quality of the final product.
Conclusion: The Future of Small-Scale Hemp Projects
Small-scale hemp projects offer a promising opportunity for farmers and entrepreneurs to tap into the growing hemp market and generate revenue. These projects have several advantages over large-scale operations, including lower capital investment, greater flexibility, and sustainability. Proper planning and execution are critical to ensure the success of small-scale hemp projects, from selecting the appropriate strain to harvesting and processing the crop. Technology can also play a significant role in maximizing yields and efficiency in these projects. With the increasing demand for hemp-derived products, the future of small-scale hemp projects looks bright.





















 Home(1)
Home(1)




