Link: GRC Explained
Yulia Landbo
Yulia Landbo
Last updated: Jul 19, 2023 · 6 min read
As businesses continue undergoing change across all sectors today, one constant remains: the necessity for efficient governance alongside effective risk management and rigorous compliance with rules and regulations (also known as GRC). Amidst dynamic technological advances and ever-evolving regulatory landscapes, GRC has emerged as a fundamental pillar of successful businesses, fostering resilience, sustainability, and the ability to thrive despite challenges.
But what does GRC entail, and why has it become an essential aspect for organizations today? This blog post will delve into the nature of GRC, exploring its components, key benefits, and its integral role in the modern business landscape.
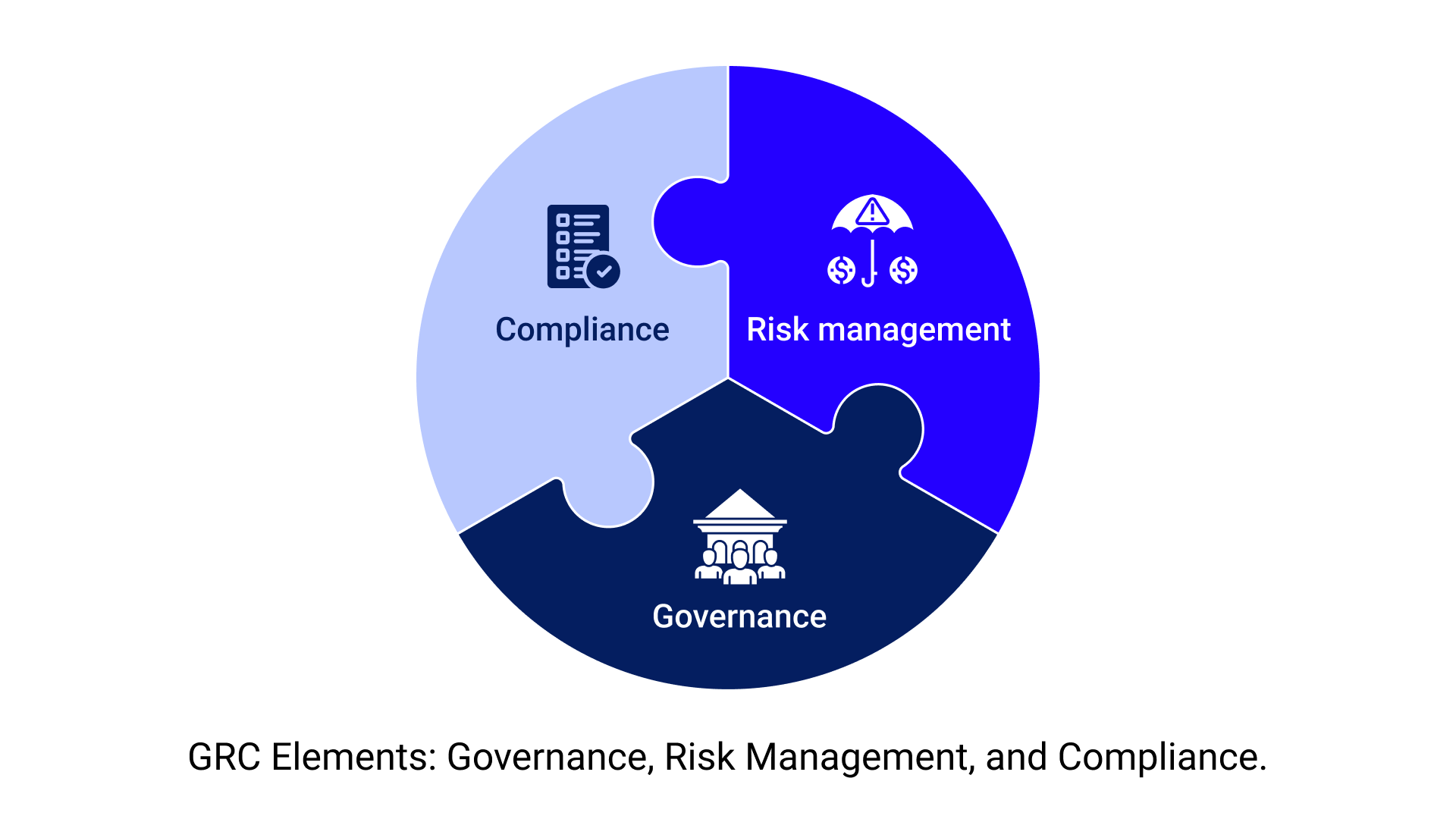
Understanding GRC
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance, or GRC, is a strategic framework implemented by organizations to align business objectives with operational processes and procedures, manage risks effectively, and ensure compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Governance entails the overall management approach adopted by executives to manage every department within an organization. Governance functions are vital in making sure that critical management information reaching the executive team is complete, accurate, and timely for decision-making and ensure that strategies and directions from the management are carried out effectively;
- Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats to an organization. These risks could stem from various sources, such as financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, strategic management errors, accidents, and natural disasters;
- Compliance refers to the organization’s adherence to regulatory requirements for business operations, data protection, and staff conduct. It also includes adherence to internal policies and procedures to protect the business and its stakeholders.
Serving as an integrated, holistic approach to business operations, governance, risk, and compliance practices contributes to:
- Improved decision-making,
- Optimal IT investments,
- Better communication,
- Proactive management of operational and strategic risks, etc.
Organizations can achieve their objectives, ensure accountability, and manage risks efficiently through good governance, rigorous risk management, and strict compliance.
The Significance of Governance
Governance refers to the set of policies, regulations, functions, processes, procedures, and responsibilities that define an organization’s establishment, management, and control. It lays the groundwork for how a company operates, and therefore, investing in solid governance is a critical step toward achieving organizational excellence.
Governance in GRC
Within the GRC framework, governance acts as the guiding principle that aligns and integrates the aspects of risk management and compliance. Its main functions are to:
- Define the corporate structure and management hierarchies,
- Set strategic objectives,
- Establish operating principles and ethical standards,
- Monitor the performance of both management and the organization.
Laying the foundation for effective governance
Establishing effective governance structures is crucial for an organization’s longevity and success. It ensures transparency, predictability, and a system of checks and balances, which are essential to maintaining stakeholder trust. With a robust governance framework, organizations can avoid unnecessary risks and manage existing ones more effectively. Furthermore, such a framework can improve organizational efficiency by providing clear lines of authority and responsibility, ensuring optimal use of resources.
Oversight towards organizational excellence
Governance plays a crucial role in:
- Decision-making: through clearly defined policies and procedures, governance provides a roadmap for making critical decisions that align with the organization’s mission, vision, and strategic goals;
- Strategic planning establishes the mechanisms for executing strategic initiatives, ensuring that these initiatives are in the organization’s best interests and contribute to achieving its objectives;
- Organizational oversight. Governance helps ensure that all activities align with the organization’s strategy and comply with legal and ethical standards. This oversight function includes monitoring performance, implementing controls, managing risks, and ensuring compliance, collectively contributing to organizational excellence.
The Role of Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial component that detects, evaluates, and controls threats to an organization. Risk management is an integral part of the GRC framework, providing the methodologies and procedures that integrate with governance to manage risks and ensure compliance.
Unpacking the risk management process
The risk management process is typically broken down into four key steps, as follows:
- Risk identification involves recognizing potential events or conditions that could negatively impact the organization’s objectives. These include financial risks, operational risks, strategic risks, and more.
- Risk Assessment. Once detected, these risks are assessed depending on the likelihood of occurrence and potential consequences. This allows organizations to prioritize risks and invest their efforts appropriately.
- Risk Mitigation involves creating strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This could include implementing new procedures, investing in new technologies, or changing business strategies.
- Risk Monitoring involves constantly reviewing and updating the organization’s risk profile, including the effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and making necessary updates as conditions change.
The strategic value of risk management
Risk management plays a vital role in minimizing potential threats and maximizing opportunities. By identifying and assessing potential risks, organizations can devise strategies that prevent these risks from materializing and turn them into opportunities for growth and improvement.
In the context of GRC, when done effectively, risk management can protect an organization from surprises, enhance resource allocation, boost stakeholder confidence, and ultimately drive organizational success.
The Importance of Compliance
The final piece of the GRC puzzle is compliance, which refers to the organization’s adherence to relevant laws, industry standards, and internal policies. Compliance is a crucial aspect of GRC, ensuring a business operates within the boundaries set by external bodies and internal guidelines.
Why compliance matters in the GRC landscape
Within the GRC framework, compliance works in tandem with governance and risk management to create a comprehensive approach to business operations. Effective governance structures provide the foundation for compliance, outlining the policies and procedures necessary to meet relevant regulatory standards. On the other hand, risk management helps identify compliance risks and devise strategies to mitigate them, ensuring the organization stays on the right side of the law and upholds its reputation.
Regulations, standards, and policies – key pillars
Regulatory compliance involves adhering to laws and regulations applicable to the organization’s operations. These can range from data protection and privacy laws to labor standards and environmental regulations.
Industry standards are guidelines and norms established by industry bodies to maintain quality and safety benchmarks. Compliance with these standards is often voluntary but can significantly enhance an organization’s credibility and competitiveness.
Internal policies are procedures set by the organization itself. These may include ethical guidelines, HR policies, or data management policies. Compliance with internal policies is crucial to maintaining organizational integrity and ensuring smooth operations.
Unpacking the implications of non-compliance
Non-compliance carries significant risks and can have severe implications for an organization, such as hefty fines, legal penalties, and in extreme cases, closing down business operations.
Beyond the legal consequences, non-compliance can also cause severe reputational damage. In an era where transparency and corporate responsibility are highly valued, any failure to comply with legal or ethical standards can diminish customer trust, which can be time-consuming, complex, and costly to rebuild.
Moreover, non-compliance can also lead to operational and financial risks. It can disrupt business operations, lead to financial losses, and sometimes even threaten the organization’s survival.
Key Benefits of GRC Implementation
Implementing a comprehensive governance, risk, and compliance framework provides many advantages that strengthen the overall operational structure of an organization and contribute to its strategic goals. These advantages include:
- Improved decision-making
Improved decision-making can be achieved through enhanced information management and data analysis. By integrating governance, risk, and compliance, organizations can ensure that all relevant information is accessible and analyzed thoroughly, providing a holistic view of the business. This, in turn, allows decision-makers to make informed strategic decisions that align with the organization’s objectives and risk tolerance while also ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Improved organizational resilience
By providing a structured approach to risk management, GRC empowers businesses to proactively identify potential risks, estimate their impact, and develop and implement effective mitigation strategies. This enhances the organization’s resilience, enabling it to recover more quickly and effectively if disruptions occur.
- Reduced compliance violations and associated costs
Compliance is essential to GRC, and a well-integrated approach can significantly reduce compliance violations. By streamlining and automating compliance processes, organizations can ensure that all relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies are adhered to consistently and effectively. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties, as well as lowers the cost of compliance by eliminating redundancies and improving efficiency.
Best Practices for GRC Implementation
Integrating a GRC approach requires careful planning, dedicated resources, and ongoing commitment. Here are some best practices for effective governance, risk, and compliance implementation:
- Establishing a GRC framework tailored to the organization’s needs
Every organization is unique, with its own set of objectives, risks, and regulatory requirements. As such, implementing a GRC approach requires developing a framework based on the organization’s specific needs, understanding the organization’s strategic objectives, as well as identifying potential risks and compliance requirements.
- Engaging stakeholders and fostering a culture of accountability and compliance
Governance, risk, and compliance are not solely the responsibility of the organization’s leadership or a dedicated GRC team; it involves everyone in the organization. As such, engaging all stakeholders is crucial in the GRC process. This consists in communicating the importance of GRC, providing appropriate training, and fostering a culture of accountability and compliance.
- Constant monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of GRC processes
GRC is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. Organizations should regularly review their governance, risk, and compliance processes to ensure they remain effective and aligned with their evolving objectives, risks, and compliance requirements. This includes overseeing the deployment of governance frameworks and processes, evaluating risk management strategies, and ensuring compliance with regulations and policies.
In a complex business landscape, embracing GRC is more than managing risks or ensuring compliance. It’s about setting the organization on a path to success. As such, governance, risk, and compliance should be a priority for every organization seeking to thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape and scale new heights of operational excellence.
Link: GRC Explained


 Home(1)
Home(1)




